|
|
A summary of the drilling processAn oil well is created by drilling a hole 5 to 36 inches (127.0 mm to 914.4 mm) in diameter into the earth with a drilling rig, which rotates a drill string with a bit attached. These are the key steps involved in drilling a well: - The drill bit, assisted by the weight of drill string and drill collars above it, breaks up the earth. - Drilling fluid (‘mud’) is pumped down the inside of the drill pipe and exits at the drill bit, helping to break up the rock, keeping pressure on top of the bit, as well as cleaning, cooling and lubricating the bit. - The generated rock ‘cuttings’ are swept up by the drilling fluid as it circulates back to the surface outside the drillpipe. - The cuttings and returning fluids are monitored for abnormalities to detect any possible ‘kicks’ in pressure. - The pipe or drillstring to which the bit is attached is gradually lengthened as the well gets deeper by screwing in several 30-foot (10 m) joints of pipe at the surface. This process is all facilitated by a drilling rig which contains all necessary equipment to circulate the drilling fluid, hoist and turn the pipe, control down hole pressures, remove cuttings from the drilling fluid and generate onsite power for these operations. The first oil wells were drilled in China in the 4th century or earlier. They reached depths of up to 243 metres and were drilled using bits attached to bamboo poles. The Middle East’s petroleum industry was established by the 8th century, when the street of the newly constructed Baghdad were paved with tar, derived from petroleum that became accessible from natural fields in the region. The first modern oil well was drilled in 1848 by Russian engineer F.N. Semyonov on the Asheron Peninsula north-east of Baku. By 1861, Baku produced about 90% of the world’s oil. The word ‘petroleum’ derives from two Greek words meaning ‘rock oil’. When Edwin Drake struck oil in the first US discovery in 1859, he was actually boring for salt. Until the 1970s, most oil wells were vertical. Using deviated and horizontal drilling it has become possible to reach reservoirs several kilometers away from the drilling place.
Задание 2. Заполните таблицу и задайте вопросы с этими словами как в примере: Task 2. Complete the table and ask questions, using these words as in example: Example: How long is the pipeline? What is the length of the pipeline?
Задание 3. Заполните эти вопросы словами из рамки. Начните вопрос со слов 'What is the ...?' или 'How ...?: Task 3. Complete these questions using words from the box. Start each question with 'What is the ...?' or 'How ...?:
1. Q: _____ is the well? A: There are several wells on this rig. The deepest is around 4,500 metres. 2. Q: _____ at that depth? A: It can be as much as 15,000 psi, which is why we have a BOP to prevent blowouts. 3. Q: _____ of the derrick? A: It is approximately 40 metres from the crown block to the working floor. 4. Q: _____ of the derrick? A: It can withstand wind speeds of anything up to 125 miles per hour. 5. Q: _____ of the hole? A: The hole gets narrower as you go down, but at the surface it is more or less 50 cm. 6. Q: _____ are the drillpipes? A: These pipes are made of steel with a thickness of just under 1 cm. 7. Q: _____ are the drillpipes? A: Each joint is roughly 10 metres in length. If they are all the same, it makes storage much easier. 8. Q: _____of a diamond bit? A: They are extremely expensive, ranging from $12,000 to $15,000 each.
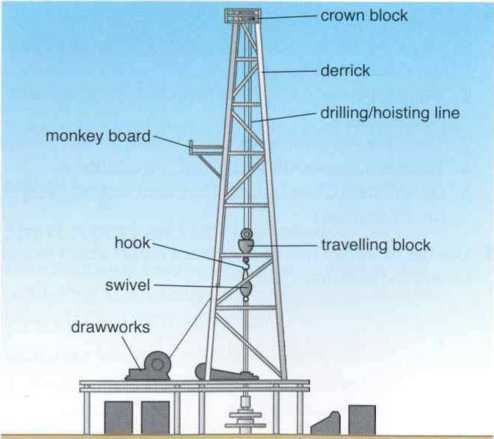
Задание 4. Изучите диаграмму буровой вышки и соедините описание со словами в диаграмме: Task 4. Study the diagram of a drilling rig and match the descriptions to the words in the diagram:
Example:This raises and lowers drilling equipment in and out of the well, hoisting line. 1. The swivel and the drilling equipment are all suspended from this.…. 2. The hoisting line goes around this piece of equipment. When it turns, the line goes up or down….. 3. This is the steel tower that goes over the well. All the lifting and drilling equipment is inside it. ..... 4. This connects two objects. It allows the one below to rotate, and the one above to stay still. ….. 5. This is the small platform near the top of the derrick where the one of the drilling team stands….. 6. This is the frame and wheels that move up and down the derrick on the hoisting line….. 7. This is the steel frame and wheels that are fixed on top of the derrick…..
Задание 5. Прочитайте и переведите текст: Task 5. Read and translate the text: The drill string The work of drilling under the ground is performed by the drill string. The drill string consists of the kelly, sections of drill pipe, the drill collar, and a bit to drill the rock. The kelly is a strong pipe that is always at the top of the drill string. It has four or six sides and goes through the rotary table which turns around (rotates). The rotary table is on the drill floor. There are many lengths of drill pipe between the kelly and the drill collar. Oil workers add sections of drill pipe one by one to the kelly. Each time they add a section, they lift the kelly out of the hole. Then they add a section of ll pipe at the top of the string and lower it back into the ground. At the bottom of the string we can find the drill collar. The bit goes into the collar. Bits are usually tricone – in other words, they have three rotating cones. A circular bit with a hole in the middle is used to take core samples. Drill bits can be covered with industrial diamonds to make them last longer. Drilling mud is pumped through jets in the bit - this lubricates and cools it and, as the mud is circulated, it also carries the pieces of drilled rock fragments to the surface. Задание 6. Закончите предложения: Task 6. Complete these sentences: 1. The crown block is _____ the top of the derrick. 2. The drill collar is _____ the bit and the drill pipe sections. 3. A member of the crew stands _____ the monkey board. 4. The kelly goes _____ the rotary table. 5. The hoisting line goes _____ the draw works. 6. The swivel is _____ the hook.
Задание 7. Соедините вид работы с его описанием : Task 7. Match the jobs with the descriptions: 1. company man a. is in charge of the engines, 2. drill pusher b. is a general helper, 3. derrick man с. looks after the mud supply, 4. mud man d. leads the drilling team, 5. motor man e. is second in command, 6. roustabout f. represents the oil company, 7. roughneck g. handles the pipes.
Практическое занятие 13 Rotating Systems Вращающиеся системы
bottom hole забой drill bit буровая коронка, головка бура drill collar удлинитель, воротник бура tubular цилиндрический, полый sub переводник, переходная муфта logging каротаж drillpipe бурильная труба drillstring бурильная колонна extend удлинять deviate отводить, отклонять joint трубка, замок cone конус, колокол, коническая насадка wear out изнашивание screw завинчивать, привинтить rotate бурить, вращать
Task 1. Read and translate the text: Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст: Rotating Systems The bottom hole assembly (BHA) is made up of a drill bit which is used to break up the rock formations, drill collars (which are heavy, thick-walled tubulars used to apply weight to the drill bit) and subs (smaller sections of pipe), such as stabilizers, which keep the drilling assembly centred in the hole. The BHA may also contain other components, such as a down hole motor, Rotary Steerable System, measurement while drilling (MWD) and logging while drilling (LWD) tools. Heavyweight drill pipe (HWDP) is used to make the transition between the drill collars and drill pipe. The function of the HWDP is to provide a flexible transition between the drill collars and the drill pipe. This helps to reduce the number of fatigue failures seen directly above the BHA. A secondary use of HWDP is to add additional weight to the drill bit. Drill pipe makes up the majority of a drill string. A drill string is typically about 15,000 feet in length for an oil or gas well vertically drilled onshore in the United States, and may extend to over 30,000 feet for an offshore deviated well. The components of the string are joined together with special threaded connections known as tool joints, on the ends of each joint. Drill tubulars are manufactured in 31-foot lengths, although they can also be manufactured in 45-foot lengths. Each 31-foot component is referred to as a joint. Typically, two, three or four joints are joined together to make a stand. Pulling the drill string out of or running the drill string into the hole is referred to as tripping. Drill pipe, HWDP and collars are typically tripped in stands to save time. This is a device used for safe automated handling of double or triple stands. There is a typical tricone drilling bit. In today's modern industry, the two main types of drill bits are classed as PDC (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact) and Roller Cone; although the tricone dominates, bicone and mono cone bits do exist. Natural and synthetic diamonds are used in coring bits, as well as for very hard rock drilling with mud motors and turbines.
Task 2.Identify the following items of equipment mentioned in reading task 1: Задание 2. Определите, к какому оборудованию из текста для чтения 1 относятся следующие детали: 1. Threaded connections used for joining together the different parts of the string. 2. An outer layer of piping thick enough to withstand the pressure of the sea, down circulation fluids can be passed. 3. A steel and concrete shoring used in a formation to protect the walls of the well. 4. The part of the bottomhole assembly used to break up rock. 5. Heavy pieces of piping which add extra weight to the bottomhole assembly. 6. Devices that enable the drillers to keep the drillstring centred in the hole. 7. The combination of all the elements used downhole in the drilling process. 8. A length of pipe, typically 31 feet long. 9. A combination of pipes and other components, connected to the string above the rig f as the string is extended. 10. A bit with three rotating parts for cutting and breaking the rock. 11. Another name for drillpipe, so-called because it is shaped like a tube. 12. These are smaller sections run between and below drill collars with various functions in the drilling process.
Task 3. Use the verbs given in the box below to complete the information about drilling bits. Use the 's' ending if you think it is necessary: Задание 3. Вставьте слова, данные в рамочке, в предложения. Используйте окончание –s там, где необходимо:
1. The bit _____ into the bit sub on the bottom of the drillstring. 2. Drilling mud _____ through channels in the bit. 3. In a rotary cone bit, the cones _____ on sealed and self-lubricating bearings. 4. The teeth or buttons on the bit _____ the rock at the bottom of the well. 5. A PDC bit is the most expensive type, but it _____ more footage in a well then any other type. 6. A bit _____ at a rate of up to 200 rpm. 7. The bit ______ cuttings which are washed back up to the surface by the drilling. 8. A tricone bit _____ and needs to be replaced after 8 to 200 hours of drilling. 9. When a bit has worn out, rate of penetration _____ and the drillpipe _____ a different noise on the drilling floor.
Task 4. Read and translate the text. Ask your own questions: Задание 4. Прочитайте и переведите текст. Задайте несколько вопросов по теме: How does the drillstring rotate? Thanks a lot Dieter, that's a good question. First of all, I will explain the traditional rotating system and then we can look at some of the latest technological developments. As you know, there is a hook attached to the hoisting line below the travelling block. Well, attached to the hook is a swivel, which in turn connects to the drillstring. Below that is a heavy four or six-sided pipe called the kelly, which is gripped by something known as the kelly bushing, which in turn fits into the master bushing of the rotary table. The kelly is connected to the drillstring, and so when the rig is powered up, all the components rotate together as a unit. Is that clear? Good ... now let's look at some of the recent developments in power systems…
Практическое занятие 14 Circulating Systems Циркуляционные системы drilling fluid буровой раствор rock cuttings шлам pit резервная яма, колодец caving образование пустот, обвал стенок скважины film пленка, тонкий слой seal уплотнять, закупоривать, герметизировать weighting material уплотнитель, утяжелитель lubricate смазывать, делать скользким cool охлаждать bearings опоры barite барит, тяжелый шпат environment окружающая среда circulating system циркуляционная система
Task 1. Read the introduction to the uses of mud on a drilling rig and underline two or three words that best summarize the main point of each use: Задание 1. Прочитайте текст об использовании буровой жидкости. Выберете два, три слова, которые резюмируют главную идею текста: Drilling fluid Drilling fluid (often called 'mud') is used to: lift soil/rock cuttings from the bottom of the borehole and carry them to a settling pit allow cuttings to drop out in the mud pit so that they are not recirculated (influenced by mud thickness, flow rate in the settling pits and shape/ size of the pits) prevent cuttings from rapidly settling while another length of drillpipe is being added (if cuttings drop too fast, they can build up on top of the bit and seize it in the hole) create a film of small particles on the borehole wall to prevent caving and to ensure that the upward-flowing stream of drilling fluid does not erode the formation seal the borehole wall to reduce fluid loss (minimizing volumes of drilling fluid is especially important in dry areas where water must be carried from far away) keep underground pressures in check by adding weighting materials, such as barite, to the fluid cool and clean the drill bit lubricate the bit, bearings, mud pump and drillpipe.
Task 2. Read and translate the text: Задание 2. Прочитайте и переведите текст: Types of drilling fluid Water-Based Fluids Baker Hughes Drilling Fluids’ high performance water-based muds (HPWBM) are designed to emulate the performance attributes of invert-emulsion systems. The need for environmentally safe and technically equivalent, water-based alternatives to emulsion systems is increasingly becoming an important consideration in the drilling fluid selection process. Baker Hughes I' ling Fluids was the first service company to introduce HPWBM, starting with the AQUA-DRIILL SystemSM, in the early 1990s. We have continually researched technology to constantly improve high performance water-based muds. New technology such as MAX-SHIELDSM and MAX-PLEXSM, which improves shale stability, and MAX-GUARDSM, which suppresses the hydration and dispersion of heavy reactive clays, have proven to be significant performance-enhancement products in our high performance water-based product line. Specialty Fluids As the drilling industry matures and the search for hydrocarbons moves into even more challenging environments, the need for innovative and novel drilling solutions takes on neater importance. The utilization of specialized drilling fluid additives is becoming more prevalent, especially in depleted fields and in deep and ultra deep waters. These challenging wells require more than just traditional additives to successfully achieve the goal of moving oil d gas from the reservoir into the refining process. Baker Hughes Drilling Fluids offers a complete line of innovative specialty products for every drilling need. From basic components for controlling lost circulation, maintaining shale control and providing downhole lubricants, to the more exotic products designed to prevent 4'ential sticking in demanding wells, no problem is too large or too small. BHDF’s product portfolio includes lost circulation materials, lubricants, ROP enhancers, sophisticated shale control products, and most importantly, spotting fluids. Since its first successful application in the 1940s, Baker Hughes Drilling Fluids’ BLACK MAGIC™ spotting fluid has been widely recognized as the drilling industry’s best product for successfully freeing differential stuck pipe. Emulsion Fluids Baker Hughes Drilling Fluids is on the forefront of developing synthetic-based compliant emulsion systems for drilling in challenging downhole conditions, such as deep-water and (high pressure – high temperature). The developments were driven by the extreme HPHT environment associated with Deep Shelf drilling in the Gulf of Mexico and the deviated HPHT wells drilled in the North Sea. Laboratory testing demonstrates fluid stability at temperatures in excess of 580°F and pressures exceeding 30,000 psi. Since 2001, Baker Hughes Drilling Fluids has been working on perfecting a major change in HPHT emulsion-based systems. Although the revision was initially triggered by environmental legislation changes in the North Sea area, the developments and improved chemistries have demonstrated superior performance in both diesel-based fluids and in the synthetic fluids used r e Gulf of Mexico (GOM) and other areas. The chemistries chosen deliver minimal impact on the environment and to the health and safety of the personnel involved.
Task 3. Read the text. Use English-Russian dictionary to give Russian equivalents to the following words: Задание 3. Прочитайте текст, пользуясь словарем, дайте русские эквиваленты следующим словам и выражениям: swivel, kelly, drillpipe, wellbore, drill colar, bit, rotary hose, mud mixer, stand pipe, discharge, mud suction line, reserve pit.
During drilling, a multi-purpose fluid known as 'mud' is circulated in the borehole. Large quantities are required for the circulating system, and there are strict rules governing the chemicals which can be used because of potential environmental impacts. On a drilling rig, mud is pumped from the mud pits through the drillstring where it sprays out of nozzles on the drill bit, cleaning and cooling the drill bit in the process. The mud then carries the crushed rock ('cuttings') up the annular space ('annulus') between the drillstring and the sides of the hole being drilled, up through the surface casing, and emerges back at the surface. Cuttings are then filtered out at the shale shakers and the mud returns to the mud pits. The returning mud can contain natural gases or other flammable materials. These can collect in and around the shale shakers area or in other work areas, so safety procedures have to be in place and special monitoring sensors and explosion-proof certified equipment have to be installed. The mud is pumped back down hole and is continuously recirculated. After testing, the mud is treated periodically in the mud pits to give it properties that optimize and improve drilling efficiency.
Task 4. Decide if the following statements are true (T) or false (F). If the statement is false, see if you can correct it: Задание 4. Определите, соответствуют ли высказывания тексту или нет. Если нет, сделайте необходимые исправления: a) Mud travels from the mud pit, down the drill string and out of the drill bit. b) The mud carries the cuttings back up the drill string to the surface. с) The shale shakers are used to mix the mud. d) Mud can be dangerous after it has been down hole. e) Dangerous mud is disposed of. f) Drilling efficiency can be enhanced by adding supplementary fluids. Task 5. Put each phrase in the correct column in the table below: Задание 5. Распределите следующие высказывания в таблицу: The following phrases in the box refer to either: – the functions of mud (i.e., what it does during the drilling process) – the properties of mud (i.e., why it is used for these functions and how it can be altered to enhance its functionality) – the ingredients of mud (i.e., what it contains)

Не нашли, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском по сайту: ©2015 - 2025 stydopedia.ru Все материалы защищены законодательством РФ.
|