|
|
Read and translate the text with a dictionaryNEUROPHARMACOLOGIC DRUGS
These drugs act on the nervous system. There are two major types of neuropharmacologic drugs: autonomic drugs and central nervous system drugs. Autonomic Drugs. These drugs influence the body in a manner similar to the action of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves of the autonomic nervous system. The function of the sympathetic nerve network in the body is (1) to stimulate the flow of epinephrine from the adrenal gland, (2) to increase heart rate, (3) to constrict blood vessels, and (4) to dilate air passages. Drugs which mimic the action of sympathetic nerves are called sympathomimetic or adrenergic agents. They stimulate the flow of epinephrine, increase heart rate, constrict blood vessels, and dilate air passages. Examples of sympathomimetic drugs are epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). These drugs are the same chemicals which are naturally released from the sympathetic nerve endings and adrenal glands during times of stress emergency. Drugs which mimic the action of parasympathetic nerves are called parasympathomimetic or cholinergic agents. These drugs oppose the actions of the sympathomimetic (adrenergic) drugs, which means that they slow down heart rate, constrict air passage, and stimulate involuntary muscles in the digestive tract and other organs. The parasympathetic agent which is produced normally at all times by parasympathetic nerve endings is called acetylcholine. Acetylcholine, unlike a drug such as epinephrine (adrenaline), cannot be administered to patient. This is because there are enzymes in the body called cholinesterases which inactivate acetylcholine almost as quickly as it is given. Other cholinergic drugs are, therefore, chosen as exogenous agents. One example of a cholinergic drug similar to acetylcholine in effect but longer lasting in the body is bethanechol. Bethanechol (Urecholine) is used in postoperative urinary retention to include the constriction of the urinary bladder, aiding urination. Other autonomic drugs are parasympatholytic agents which oppose the effect of parasympathetic nerve stimulation. Examples of these drugs are atropine and belladonna, which are also known as antispasmodic drugs because they act to relax the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract and decrease peristalsis. Sympatholytic agents, which block the action of the sympathetic nervous system, include reserpine, guanethidine, and phentolamine. These drugs are used to decrease blood pressure and protect against the excess epinephrine secretion liberated by pheochromocytomas (tumors of the adrenal gland).
(Make a chart summarizing various types of autonomic drugs.)
Texts for written translation Read the text using a dictionary ANTIHISTAMINES These are drugs which block the action of a chemical called histamine which is found in the body. Histamine is produced by most cells and especially by sensitive cells under the skin and in the respiratory system. When certain foreign antigens (protein substances which lead to the production of antibodies) enter the body, antibodies are made by cells. These antibodies attempt to inactivate, or neutralize, the offending antigens and, as a result, a chemical called histamine may be released by other cells. Histamine causes the characteristic allergic symptoms when it is liberated from cells: itching, hives, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, high fever, and, in some very serious cases, anaphylactic shock. Antihistamines, by blocking the action of histamine in the body, can relieve the allergic symptoms which histamine produces. Antihistamines cannot cure the allergic reaction, but they can relieve its symptoms. Some potentially dangerous side effects of antihistamines are drowsiness, sedation, and blurred vision. Examples of antihistamines are diphenhydramine (Benadryl), meclizine (Bonamine), chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trime-ton) and tripelennamine (Pyribenzamine). Make up 5 questions about the contents of the text Drug Package
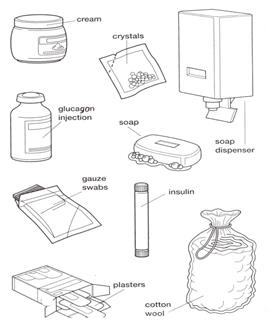
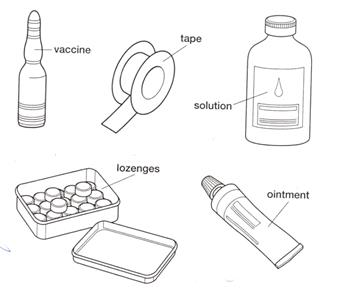
Ex 1. Прочитайте следующие слова: cream – крем crystals – кристаллы glucagon injection – ампула для инъекций глюкагона soap – мыло soap dispenser – мыльница gauze swabs – марлевые тампоны insulin – ампула с инсулином plasters – пластырь cotton wool – вата vaccine – ампула с вакциной tape – роликовый пластырь solution – раствор lozenges – пастилки ointment – мазь
Ex 2. Назовите:
1. Лекарства используемые для инъекций; 2. Упаковку для кремов, растворов, мазей, пастилок и пластырей.
Ex 3. Переведите на английский язык. 1. Мази и кремы втираются для смягчения кожи и в качестве противозудного средства. 2. Раствор инсулина вводится через инъекцию внутримышечно. 3. Марлевые тампоны и вала применяются при хирургических процедурах. 4. Мыло – необходимое средство для удаления микроорганизмов с рук врача. 5. Мыло может находиться либо в мыльнице (soap box) либо в механическом распределителе (mechanical dispenser) 6. Ампулы содержат определённое количество стерильного медикамента.

Не нашли, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском по сайту: ©2015 - 2026 stydopedia.ru Все материалы защищены законодательством РФ.
|