|
|
UNIT 4. Geothermal energyCOMPREHENSION READING Task 1.Read the following words and word combinations paying attention to the correct pronunciation, write them down and learn by heart. To develop – разрабатывать, развивать, совершенствовать Trapped – защемленный Drilling – бурение, сверление Brine – минеральный раствор, соляной раствор, минеральная вода Siting – размещение Land subsidence – оседание почвы Affect – оказывать влияние, воздействовать Closed-loop system – замкнутая система Well – шахта, источник To inject – инжектировать, впрыскивать, впускать Scrubber – газоочиститель Advantage – преимущество To require – требовать Supply – поставка, подача To arouse intense opposition – встречать сильное сопротивление To expand – расширять(ся), распространять(ся) Reasonable – приемлемый, справедливый To provide – обеспечивать Scenic – живописный Task 2. Read and translate the text, define its main idea. Geothermal energy is heat contained below the earth's surface. The only type of geothermal energy that has been widely developed is hydrothermal energy, which consists of trapped hot water or steam. However, new technologies are being developed to exploit hot dry rock (accessed by drilling deep into rock), geopressured resources (pressurized brine mixed with methane), and magma. The various geothermal resource types differ in many respects, but they raise a common set of environmental issues. Air and water pollution are among the most urgent concerns, along with the safe disposal of hazardous waste, siting, and land subsidence. Since these resources would be exploited in a highly centralized fashion, reducing their environmental impacts to an acceptable level should be relatively easy. But it will always be difficult to site plants in scenic or otherwise environmentally sensitive areas. The method used to convert geothermal steam or hot water to electricity directly affects the amount of waste generated. Closed-loop systems are almost totally benign, since gases or fluids removed from the well are not exposed to the atmosphere and are usually injected back into the ground after giving up their heat. Although this technology is more expensive than conventional open-loop systems, in some cases it may reduce scrubber and solid waste disposal costs enough to provide a significant economic advantage. Most geothermal power plants will require a large amount of water for cooling or other purposes. In places where water is in short supply, this need could raise conflicts with other users for water resources. The development of hydrothermal energy faces a special problem. Many hydrothermal reservoirs are located in or near wilderness areas of great natural beauty such as Yellowstone National Park and the Cascade Mountains. Proposed developments in such areas have aroused intense opposition. If hydrothermal-electric development is to expand much further in the United States, reasonable compromises will have to be reached between environmental groups and industry. Task 3.Give the full answers to the following questions according to the text. 1) What is geothermal energy and what are its sources? 2) What environmental issues are raised by geothermal energy development? Task 4. Decide whether the given statements are true or false. You may use any of the following phrases: That is true/that’s not true I agree with this statement/I can’t agree with it The information is correct /the information is false There is no mistake in this statement /there is a mistake in this statement 1) Hydrothermal energy is the most developed type of geothermal energy. 2) With new technologies geothermal development produces no air or water pollution. 3) In closed-loop systems gases are injected back into the ground. 4) Conventional open-loop systems are less expensive than closed-loop systems. 5) Siting of hydrothermal power plants in wilderness areas arouses intense opposition. Task 5.Compose an interview between a reporter and a director of geothermal power plant. Discuss the present situation in geothermal power industry and its possible further development. VOCABULARY EXERCISES Task 1. Find in the text corresponding equivalents to the following words. Разомкнутая система, получать доступ, сухая порода, природный заповедник, столкнуться с проблемой, использовать/разрабатывать, предлагать, ресурсы, находящиеся под давлением земной коры. Task 2. Match each of the given words with its definition and translate.
Task 3. Make pares of synonyms taking one word form A and another one from B. A: to consist, various, a pollution, a fashion, to reduce, to affect, costs, to face. B: to decrease, a contamination, to encounter, a manner, to be made up of smth., different, to act on smth., expenses. GRAMMAR EXERCISES Task 1. A) In the text find the sentences in Passive voice and translate them. B) In the text find adjectives in comparative and superlative degree and translate them. Make degrees of comparison using the following adjectives and adverbs: Hot, deep, widely, much, safe, frequently, easy, sensitive, late, well, difficult, (a) little, hazardous, benign, comfortably, correctly. Task 2. Choose the right variant. 1) In Mumbai court ordered the release of five blind lions ___ for a circus. A performed B performing C are being performed D will be performed 2) Both fossil and nuclear fuels produce a great amount of ___ substances. A to pollute B pollute C polluted D polluting 3) We should inquire into the problems ___ with non-renewable energy sources. A to associate B associate C associated D associating 4) Water may ___ costly or scarce in desert areas. A to be B be C been D being 5) The world has ___ to renewable energy sources. A to switch B switch C switched D switching 6) Today strict environmental standards ___ for evaluating renewable energy projects. A to be used B are used C were used D have been used Task 3. Make four types of questions to each of the given sentences and ask your group mates to answer them. 1) Pollution directly reduces our social welfare by denying us access to clean air and water. 2) Nowadays noise is becoming a major pollutant. 3) Some areas should be permanently removed from public or private use. Task 4.Translate the following nominative-attributive groups, try to explain their meaning in English: geothermal energy, geothermal resource types, air and water pollution, solid waste disposal costs, geothermal power plants, water resources, wilderness areas. TASKS FOR INDIVIDUAL WORK Task 1. Make correct sentences and translate them. 1) Hydrothermal, consists, trapped, water, steam, energy, of, hot, or. 2) Geopressured, include, mixed, methane, resources, with, pressurized, brine. 3) We, their, should, impacts, reduce, an, to, level, environmental, acceptable. 4) Closed-loop, are, than, more, systems, ones, benign, open-loop. 5) The, for, water, need, conflicts, raise, cooling, can, serious. Task 2. Translate the following sentences into English. 1) Существуют приборы для сокращения объема макрочастиц в воздухе, так что негативное воздействие на организм можно уменьшить. 2) Проблема в том, где можно разместить новую электростанцию, чтобы избежать критического уровня загрязнения местной природы. 3) Мы считаем, что затраты на утилизацию отходов можно снизить, используя более эффективную технологию. 4) Если развитие гидроэнергетики будет продолжаться, необходимо достичь компромисса между защитниками окружающей среды и промышленностью. 5) Хотя эта технология дороже, она дает значительное экономическое преимущество фермерам. 6) Так как многие гидротермальные источники находятся вблизи природных заповедников, это вызывает возмущение общественности. 7) Следует помнить, что большинство ГЭС нуждается в большом количестве воды для охлаждения и других целей. 8) Такая система полностью безопасна, т.к. газ и жидкость, извлеченные из шахты, впрыскиваются обратно после обработки. 9) Множество технологий было разработано с целью использования геотермальной энергии, т.е. тепла Земли. 10) Разнообразие геотермальных источников позволяет использовать их как в малых, так и в крупных масштабах. Task 3. Prepare the summary of the text.
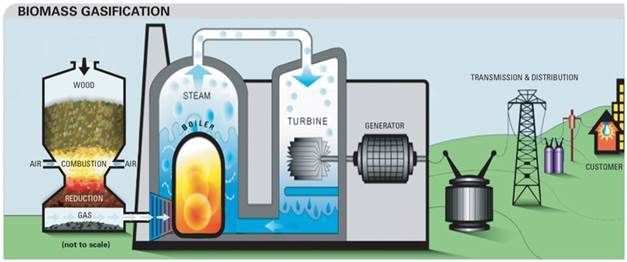
UNIT 5. Biomass COMPREHENSION READING Task 1.Read the following words and word combinations paying attention to the correct pronunciation, write them down and learn by heart. To derive from – происходить от Except – кроме Biomass-based fuels – синтетическое топливо из биомассы Conversion – переработка Inevitably – неизбежно Carbon – углерод Nitrogen – азот Particulates – (макро) частицы Soot and ash – сажа и зола (пепел) Stove – печь Electrostatic precipitator – электростатический осадитель, электрофильтр Regulation – предписание, распоряжение To enforce – усиливать Doubtful – сомнительный To catch on – становиться популярным Notable – заметный Facilities – приспособление, оборудование Sulfur – сера Mercury – ртуть Successive – следующий один за другим Gasifier – газификатор, газогенератор Task 2. Read and translate the text, define its main idea. Biomass power, derived from burning of plant matter, raises more serious environmental issues than any other renewable resource except hydropower. Combustion of biomass and biomass-based fuels produces air pollution; beyond this, there are concerns about the impacts of using land to grow energy crops. How serious these impacts are will depend on how carefully the resource is managed. The picture is further complicated because there is no single biomass technology, but rather a wide variety of production and conversion methods, each with different environmental impacts. Inevitably, the combustion of biomass produces air pollutants, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulates such as soot and ash. The amount of pollution emitted per unit of energy generated varies widely by technology. Wood-burning stoves and fireplaces generally are considered to be the worst offenders. Modern, enclosed fireplaces and wood stoves pollute much less than traditional, open fireplaces for the simple reason that they are more efficient. Specialized pollution control devices such as electrostatic precipitators (to remove particulates) are available, but without specific regulation to enforce their use it is doubtful they will catch on. Emissions from conventional biomass-fueled power plants are generally similar to emissions from coal-fired power plants, with the notable difference that biomass facilities produce very little sulfur dioxide or toxic metals (cadmium, mercury, and others). The most serious problem is their particulate emissions, which must be controlled with special devices. More advanced technologies, such as the whole-tree burner (which has three successive combustion stages) and the gasifier/combustion turbine combination, should generate much lower emissions, perhaps comparable to those of power plants fueled by natural gas. Task 3.Give the full answers to the following questions according to the text. 1) What is biomass power derived from? 2) Does burning of biomass produce pollution? If yes, what technologies help reduce it? Task 4. Decide whether the given statements are true or false. You may use any of the following phrases: That is true/that’s not true I agree with this statement/I can’t agree with it The information is correct /the information is false There is no mistake in this statement /there is a mistake in this statement 1) There are several biomass technologies with different environmental impacts. 2) Biomass power is produced when plant matter is burnt. 3) Traditional fireplaces and wood stoves are more efficient. 4) Burning of biomass produces a great amount of sulphur dioxide and cadmium. 5) There is still no technology to control particulate emissions. Task 5.Look at the picture.Compose your own dialogues and discuss the stages of biomass processing. Use these words: biomass gasification, wood, air, combustion, reduction, gas, steam, boiler, turbine, generator, transmission, distribution, customer.
VOCABULARY EXERCISES Task 1. Find in the text corresponding equivalents to the following words. Сжигание растительного материала, сгорание биомассы, помимо этого, широкое разнообразие, топливо на биомассе, удалять макро частицы, заметная разница, печь для сжигания цельного дерева. Task 2. Match each of the given words with its definition and translate.
Task 3. Make pares of synonyms taking one word form A and another one from B. A: to manage, complicated, a combustion, advanced, a problem, to continue, to seize, a lack. B: up-to-date, to go on, to control, an issue, difficult, a shortage, a burning, to stop. GRAMMAR EXERCISES Task 1. A) In the text find the sentences with Gerund, define its function and translate the sentence. You may consult the Appendix. B) In the text find the sentences with Infinitive, define its function and translate the sentence. You may consult the Appendix. Task 2. Choose the right variant. 1) One way of ___ hydrogen is to pass electric current through water. A is obtaining B will have obtained C obtaining D obtains 2) ___ a minimal quality of environment-friendly cleaning products protects your skin from harmful chemicals A have been used B using C were used D being used 3) The construction of wind turbines is ideally suited to ___ areas. A farm B farming C farmed D farmers 4) They must solve environmental problems together with ___ communities. A affect B affecting C affection D affected 5) A great amount of polluting substances ___ when burning fossil fuel. A is produced B are produced C was produced D were produced 6) More than 30 threatened species ___ during a three-year period. A is injured B are injured C was injured D were injured Task 3. Make four types of questions to each of the given sentences and ask your group mates to answer them. 1) The soil is polluted because of illegal dumping of solid wastes. 2) You should obtain general knowledge and skills in the field of new technologies. 3) One must learn a lot to become a professional ecologist. Task 4.Translate the following nominative-attributive groups, try to explain their meaning in English: biomass power, plant matter, production and conversion methods, wood stoves, pollution control devices, biomass-fueled power plants, coal-fired power plants, particulate emissions, whole-tree burner, combustion stages, gasifier/combustion turbine combination. TASKS FOR INDIVIDUAL WORK Task 1. Make correct sentences and translate them. 1) People, manage, and, resources, should, land, carefully, water. 2) There, a, of, conversion, variety, is, methods, wide, and, production. 3) Air, carbon, and, pollutants, monoxide, particulates, include. 4) Nowadays, control, are, specialized, devices, available, pollution. 5) More, will, much, advanced, lower, generate, technologies, emissions. Task 2. Translate the following sentences into English. 1) Чем больший объем биомассы сжигается, тем больше загрязняющих веществ выбрасывается в атмосферу, что может привести к образованию смога или истощению озонового слоя. 2) Сжигание биомассы высвобождает почти такое же количество углекислого газа, как и сжигание ископаемого топлива. 3) Лес до сих пор является крупнейшим источником энергии биомассы, но можно также использовать другие источники. 4) Традиционные технологии до сих пор используются в различных отраслях промышленности наряду с альтернативными технологиями. 5) Следует быть осторожным при работе с токсичными материалами. 6) Стеклянные бутылки можно перерабатывать, как и пластиковые. 7) Использование угля и нефти в качестве топлива сильно ухудшает качество воздуха. 8) Люди уничтожили значительную часть лесного массива, строя дороги и дома. 9) Материал, который должен использоваться в фотогальванических модулях, очень опасен. 10) По-видимому, солнечные электростанции не производят загрязнения воздуха. Task 3. Prepare the summary of the text. UNIT 6. Hydropower COMPREHENSION READING Task 1.Read the following words and word combinations paying attention to the correct pronunciation, write them down and learn by heart. Dam – дамба Virtually – практически Suitable – подходящий Slack – нехватка, дефицит To take up – компенсировать Revival – возобновление, восстановление To meet expectations – оправдать ожидания Peak output – максимальный объем производства To save – спасать, сохранять Endangered species – вымирающие виды Salmon – лосось, семга To decline – уменьшаться Rapidly – быстро Arduous trip downstream – трудное путешествие вниз по течению Blade – лопасть To pursue – совершать, выполнять Frequently – часто To inundate – затоплять Wildlife habitats – среда обитания диких животных Task 2. Read and translate the text, define its main idea. The development of hydropower has become increasingly problematic in the United States. The construction of large dams has virtually ceased because most suitable undeveloped sites are under federal environmental protection. To some extent, the slack has been taken up by a revival of small-scale development. But small-scale hydro development has not met early expectations. For example, a series of large facilities on the Columbia River in Washington will probably be forced to reduce their peak output by 1,000 MW to save an endangered species of salmon. Salmon numbers have declined rapidly because the young are forced to make a long and arduous trip downstream through several power plants, risking death from turbine blades at each stage. The impact of very large dams is so great that there is almost no chance that any more will be built in the United States, although large projects continue to be pursued in Canada (the largest at James Bay in Quebec) and in many developing countries. The reservoirs created by such projects frequently inundate large areas of forest, farmland, wildlife habitats, scenic areas, and even towns. In addition, the dams can cause radical changes in river ecosystems both upstream and downstream. Task 3.Give the full answers to the following questions according to the text. 1) Why has the development of hydropower become problematic in the USA? 2) What is the impact of dams on the river ecosystems and surrounding areas? Task 4. Decide whether the given statements are true or false. You may use any of the following phrases: That is true/that’s not true I agree with this statement/I can’t agree with it The information is correct /the information is false There is no mistake in this statement /there is a mistake in this statement 1) Hydropower plants are rarely built in the USA. 2) Small scale hydro development has met early expectations. 3) Salmon numbers have been reduced because of collision with turbine blades. 4) Large dams are likely to be built all over the USA. 5) Dams have no impact on wildlife habitats or river ecosystems. Task 5.Watch the video http://www.skypeenglishclasses.com/skype-english-blog/english-conversation-classes-talking-about-renewable-energy-sources-in-english/ and try to answer the following questions: 1) What two factors make it necessary for us to adapt (change) our methods of energy production and consumption without delay? 2) What can make a great contribution to the cause with little or no CO2 emissions? 3) In terms of energy consumption what is the percentage that the EU hopes to reach by 2020? 4) How much wind electricity does the EU now produce? 5) What is geothermal energy? 6) How are solar panels useful for household needs? 7) How many meters of solar panels were installed in Europe in 2006? 8) How is biomass defined in this report? 9) Why is biomass called ‘the sleeping giant.’ 10) How much is the renewable energy sector worth for the European Union annually? 11) How do governments play a crucial role in the development of the renewable energy sector? VOCABULARY EXERCISES Task 1. Find in the text corresponding equivalents to the following words. Компенсировать недостаток, в некоторой степени, не оправдать ожидания, быть вынужденным, трудное путешествие, среда обитания диких животных, живописные районы, как вверх, так и вниз по течению. Task 2. Match each of the given words with its definition and translate.
Task 3. Make pares of synonyms taking one word form A and another one from B. A: a protection, to take up a slack, a revival, to decline, rapidly, to be forced to do smth., arduous, an inundation. B: fast, a flood, to decrease, a defense, to compensate a drawback, a renewal, to be made to do smth., difficult. GRAMMAR EXERCISES Task 1. A) In the text find the sentences with Infinitive, define its function and translate the sentences. B) In the text find the sentences with Participle II, define its function and translate the sentences. Task 2. Choose the right variant. 1) There are now urgent calls for the basking sharks ___ international protection. A has been given B will be given C to be given D gives 2) Energy ___ to manufacture and install solar components. A is required B are required C required D require 3) In some countries people seize ___ their cars for the lack of petrol. A use B using C used D usage 4) People cannot protect ___ animals from accidental death. A threated B threating C threatened D threatening 5) The purpose of this device is ___ pressure. A measure B measured C measuring D to measure 6) They want wildlife ___ in this area. A to be protected B to protect C protected D protecting Task 3. Make four types of questions to each of the given sentences and ask your group mates to answer them. 1) Eight million tons of oil is spilled into the Earth’s oceans every year because of oil tanker disasters. 2) The amount of ground water containing high concentrations of toxins is constantly increasing. 3) One should have a scientific understanding of connection between nature and society. Task 4.Translate the following nominative-attributive groups, try to explain their meaning in English: small-scale development, salmon numbers, power plant, turbine blades, wildlife habitat, river ecosystem. TASKS FOR INDIVIDUAL WORK Task 1. Make correct sentences and translate them. 1) Systems and fossil current upon fuels energy depend nuclear. 2) Area wind occupy turbines a small only. 3) Most cooling plants power require water. 4) Is below geothermal heat the earth’s energy contained surface. 5) Of air biomass combustion pollution produces.Task 2. Translate the following sentences into English. 1) По некоторым оценкам ученых, в течение следующих двухсот лет люди прекратят пользоваться автомобилями из-за недостатка топлива, если только не найдут ему замену. 2) Некоторые предприятия в Вашингтоне вынуждены сократить свой максимальный объем производства, чтобы сохранить вымирающих лососей. 3) Ожидается, что в последующие двадцать лет потребление энергии значительно возрастет во всем мире, а особенно в Азии. 4) Впервые контроль автомобильных выхлопов был введен в 1966 году, чтобы сократить выбросы углеводорода и угарного газа. 5) Прежде чем работать с опасными веществами, нужно надеть защитные очки и перчатки. 6) Наша цель – защитить рабочих от воздействия токсичных веществ. 7) Несомненно относительно инертный кремний является основным материалом, используемым в солнечных элементах. 8) Они хотят, чтобы живая природа в этом регионе была под защитой. 9) Ученые обнаружили, что это напрямую зависит от климата. 10) Анализы показали, что эти вирусы опасны, но не смертельны. Task 3. Prepare the summary of the text.

Не нашли, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском по сайту: ©2015 - 2025 stydopedia.ru Все материалы защищены законодательством РФ.
|