|
|
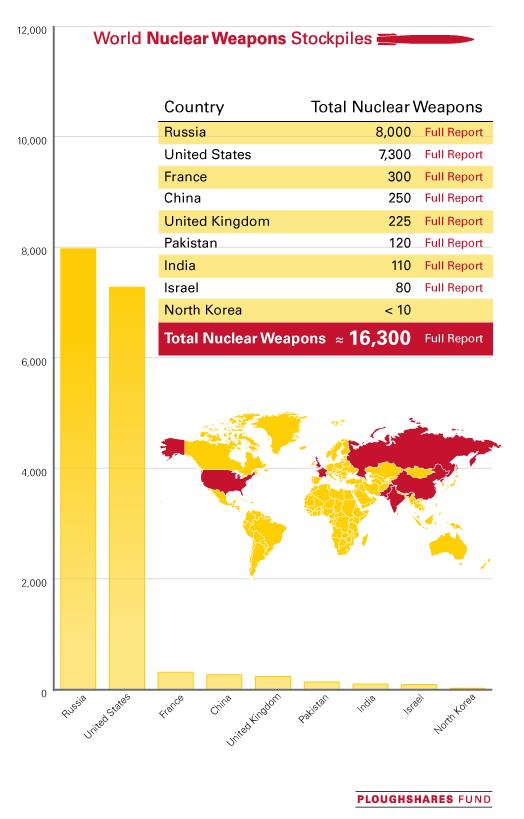
World Nuclear Stockpile Report (Updated August 28, 2014).The exact number of nuclear weapons in global arsenals is not known. With little exception, each of the nine countries with nuclear weapons guards these numbers as closely held national secrets. What is known, however, is that more than a decade and a half after the Cold War ended, the world's combined stockpile of nuclear warheads remain at unacceptably high levels.
Hans Kristensen and Robert Norris of the Federation of American Scientists are the leading experts in estimating the size of global nuclear weapons inventories. The table is a compilation of their estimates and analyses, with links to their full reports. These reports are published in The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists and discussed further at the FAS Strategic Security Blog. As the authors of these estimates note, the above numbers may not add up due to rounding and uncertainty about the operational statuses and size of the total inventories. For a full analysis of how the authors arrived at their estimates, please view the provided links for the complete reports. Nuclear arsenals Nine countries together possess more than 16,000 nuclear weapons. The United States and Russia maintain roughly 1,800 of their nuclear weapons on high-alert status – ready to be launched within minutes of a warning. Most are many times more powerful than the atomic bombs dropped on Japan in 1945. A single nuclear warhead, if detonated on a large city, could kill millions of people, with the effects persisting for decades. The failure of the nuclear powers to disarm has heightened the risk that other countries will acquire nuclear weapons. The only guarantee against the spread and use of nuclear weapons is to eliminate them without delay. Although the leaders of some nuclear-armed nations have expressed their vision for a nuclear-weapon-free world, they have failed to develop any detailed plans to eliminate their arsenals and are modernizing them.
The wider problem Five European nations host US nuclear weapons on their soil as part of a NATO nuclear-sharing arrangement, and roughly two dozen other nations claim to rely on US nuclear weapons for their security. Furthermore, there are now some 40 nations with nuclear power or research reactors capable of being diverted for weapons production. The spread of nuclear know-how has increased the risk that more nations will develop the bomb.
MODULE III TOPIC: THE UNITED NATIONS ORGANIZATION Lead in: What do you know about UN? What problems does it solve? What activities does it provide? Exercise 1 Read the text to obtain information on the topic. UN’s Birthday The name «United Nations» was devisedby United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt and was first used in the «Declaration by United Nations» of 1 January 1942, during the Second World War, when representatives of 26 nations pledgedtheir Governments to continue fighting together against the Axis Powers (Germany, Japan, and Italy). The term «United Nations» denoted those countries that were allied against the Axis powers. Soon after the end of the Second World War (1939-45), the United Nations was set up as an organization for maintainingpeace. 51 states signed its Charter –a set of rules which everyone can understand and which makes working together easier. The Charter of the United Nations was signed on 26 June 1945, in San Francisco, and officially came into force on 24 October 1945, when the Charter had been ratified by China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States and by a majority of other signatories.This day is now celebrated each year throughout the world as United Nations Day. The UN has six official languages: Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian and Spanish. Topical vocabulary
Exercise 2. Give the English equivalents to the following phrases: 1) впервые было использовано (употреблено);во время Второй мировой войны; представители двадцати шести стран; заверили, что их правительства будут продолжать; 2) совместная борьба против; вскоре после; ООН была основана (создана); сохранение мира; подписали Устав; вступил в силу; Устав был одобрен (ратифицирован) большинством; этот день отмечается; во всем мире.
Exercise 3. Give synonyms:
Exercise 4. Comprehension check: 1. Who began to use the name «United Nations» in international relations? 2. What international document contained the name «United Nations» for the first time? 3. What countries did the term «United Nations» denote? 4. What countries were called the Axis powers? 5. What document is called the Charter of the UN? When and where was it signed? 6. When is United Nations Day celebrated in the world? Why? Exercise 5. 
Не нашли, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском по сайту: ©2015 - 2024 stydopedia.ru Все материалы защищены законодательством РФ.
|